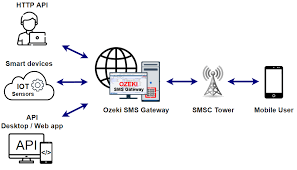
In the contemporary digital landscape, where communication sms api supreme, the efficacy of SMS (Short Message Service) stands tall as a ubiquitous tool. However, behind the scenes of seamless text message transmission lies a sophisticated mechanism known as the SMS gateway. Often overshadowed by the glamour of front-end messaging apps, the SMS gateway serves as the silent hero facilitating communication across diverse platforms. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies and significance of this technological marvel.
Understanding the SMS Gateway:
At its core, an SMS gateway is a pathway that enables the exchange of SMS messages between different telecommunication networks. It acts as a bridge, connecting various systems such as websites, applications, or email servers with the wireless carriers’ SMS centers (SMSCs). These gateways facilitate both outbound and inbound SMS traffic, ensuring seamless communication flow between disparate platforms.
Functionality and Components:
The functionality of an SMS gateway revolves around converting messages from one format to another, ensuring compatibility between different networks and systems. Here’s a breakdown of its key components:
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): APIs serve as the interface through which applications or websites communicate with the SMS gateway. Developers integrate these APIs into their systems to enable automated messaging functionalities.
- Message Routing: The SMS gateway employs sophisticated algorithms to route messages efficiently. It determines the optimal path for message delivery based on factors such as destination, carrier networks, and message priority.
- Protocol Conversion: SMS gateways perform protocol conversions to translate messages between various formats, such as HTTP, SMTP, or SMPP (Short Message Peer-to-Peer). This ensures seamless communication between different platforms.
- Message Queuing: To handle high volumes of messaging traffic, SMS gateways often employ message queuing mechanisms. Messages are queued and processed in a systematic manner, preventing bottlenecks and ensuring timely delivery.
- Error Handling: Robust SMS gateways incorporate error handling mechanisms to deal with issues such as network congestion, invalid recipient numbers, or message delivery failures. These mechanisms help in troubleshooting and ensuring message reliability.
Applications and Use Cases:
The versatility of SMS gateways extends across various industries and applications, empowering organizations to streamline communication processes and enhance customer engagement. Here are some prominent use cases:
- Marketing and Promotions: Businesses leverage SMS gateways for targeted marketing campaigns, promotional offers, and product launches. SMS marketing allows for direct and personalized communication with customers, yielding higher engagement and conversion rates.
- Authentication and Security: SMS gateways play a crucial role in two-factor authentication (2FA) and verification processes. By sending one-time passwords (OTPs) or verification codes via SMS, organizations enhance security and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access.
- Alerts and Notifications: From transaction alerts to service notifications, SMS gateways enable organizations to keep customers informed in real-time. Industries such as banking, healthcare, and logistics rely on SMS notifications for critical updates and reminders.
- Customer Support: SMS gateways facilitate two-way communication, allowing customers to initiate inquiries, raise support tickets, or provide feedback via text messages. This enhances accessibility and responsiveness, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
- Internal Communication: Beyond external communication, SMS gateways serve as a valuable tool for internal communication within organizations. From employee notifications to emergency alerts, SMS facilitates rapid dissemination of information across teams.
Future Trends and Innovations:
As technology evolves, so do the capabilities of SMS gateways. Emerging trends and innovations in this space include:
- Rich Communication Services (RCS): RCS represents the next evolution of SMS, offering enhanced multimedia capabilities such as images, videos, and interactive buttons. SMS gateways are poised to adopt RCS standards, enabling richer and more engaging messaging experiences.
- Chatbots and AI Integration: Integrating SMS gateways with AI-powered chatbots enables automated conversational interactions. Organizations leverage this integration for customer support, lead generation, and personalized messaging at scale.
- IoT (Internet of Things) Integration: With the proliferation of IoT devices, SMS gateways play a crucial role in enabling device-to-device communication. From remote monitoring to asset tracking, SMS facilitates seamless connectivity in the IoT ecosystem.
- Blockchain and Security Enhancements: Leveraging blockchain technology, SMS gateways can enhance message security, authentication, and traceability. Blockchain-based solutions ensure tamper-proof messaging infrastructure, bolstering trust and integrity.
In conclusion, the SMS gateway stands as a cornerstone of modern communication infrastructure, facilitating seamless connectivity and interaction across diverse platforms. As technology continues to evolve, SMS gateways will evolve in tandem, unlocking new possibilities and redefining the dynamics of communication in the digital age.